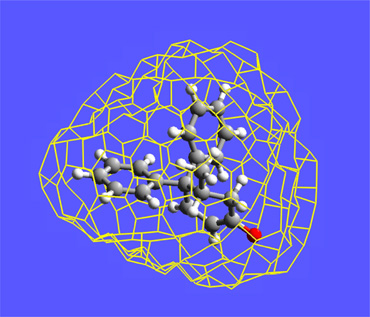
This graphic presents a computer-generated image of a molecule reacting inside a cavity made up of nonreactive gas atoms. The cavity is created by irradiation of neighboring molecules and its shape influences the course of the reaction. (From the research of Prof. Howard E. Zimmerman and Evgueni E. Nesterov, Univ. of Wisconsin, Chemistry Department, 2002.)
Highlights of this Course
Course Description
Basic principles of interaction of electromagnetic radiation, thermal neutrons, and charged particles with matter. Introduces classical electrodynamics, quantum theory of radiation, time-dependent perturbation theory, transition probabilities and cross sections describing interaction of various radiations with atomic systems. Applications include theory of nuclear magnetic resonance; Rayleigh, Raman, and Compton scattering; photoelectric effect; and use of thermal neutron scattering as a tool in condensed matter research.